Pharmacist Ekanem Mercy Obo Asuquo recently presented her research on herbal remedies for ovarian cysts and fibroids at the prestigious New York Learning Hub, captivating an audience with both rigorous data and heartfelt personal stories. In her study, Mercy explored the role of plant-based treatments as a complement to conventional therapies, offering women a more holistic approach to managing conditions that can deeply affect their daily lives.
Mercy’s research involved 133 participants who shared their journeys of using herbal remedies to ease the symptoms of ovarian cysts and fibroids. With a careful blend of statistical analysis and personal narratives, her study examined how consistent use—both in terms of dosage and duration—correlated with improvements in symptom severity. The quantitative data provided clear evidence that adherence to a structured herbal regimen can lead to notable relief, enhanced well-being, and a renewed sense of empowerment among women. Yet, it was the personal testimonies that brought the numbers to life. Women recounted their experiences of overcoming the physical discomfort and emotional distress that often accompanies these conditions, sharing how herbal treatments helped them reclaim control over their health.
In one particularly touching account, a participant described the profound relief she felt when her persistent pain began to subside, allowing her to resume daily activities that she had once thought were beyond her reach. Stories like these are a testament to the human spirit and the enduring power of natural healing methods. They reveal a side of healthcare that numbers alone cannot capture—a side that values empathy, cultural heritage, and personal choice.
Mercy’s own journey adds a compelling layer to her research. A proud graduate of the University of Ibadan, Nigeria’s premier institution where she earned her Bachelor of Pharmacy, she went on to obtain a master’s degree in public health. Her academic path continued to expand with specialized training in implementation science at the University of Washington, as well as leadership and management courses in health and business at Rome Business School. Currently, she is pursuing a dual postgraduate diploma in health and social care management from the New York Learning Hub and the Chartered Management Institute in London. Her diverse and robust background in both the scientific and managerial aspects of healthcare uniquely positions her to navigate and bridge the worlds of traditional herbal medicine and modern clinical practice.
Drawing from extensive pharmaceutical experience and a passion for scientific inquiry, Mercy has approached her research with exceptional attention to detail and a genuine care for the well-being of her participants. She has worked diligently to show that when herbal remedies are applied with precision and care, they can offer significant relief and restore hope to those who have long sought a more personalized, compassionate approach to healthcare.
Presented at a highly regarded forum in New York, this research invites clinicians, researchers, and policymakers to consider a more inclusive model of healthcare—one that recognizes the value of integrating herbal remedies with conventional treatment. Mercy Obo Asuquo’s work is a sincere contribution to a future where every patient’s experience is honored and where traditional wisdom meets modern expertise to improve lives across communities, both in Africa and around the world.
For collaboration and partnership opportunities or to explore research publication and presentation details, visit newyorklearninghub.com or contact them via WhatsApp at +1 (929) 342-8540. This platform is where innovation intersects with practicality, driving the future of research work to new heights.
Full publication is below with the author’s consent.
Abstract
Herbal Remedies for Gynecological Health: An Exploration of Plant-Based Treatments for Ovarian Cysts and Fibroids
This study investigates the potential of herbal remedies as a complementary approach to conventional treatments for ovarian cysts and fibroids, two prevalent gynecological conditions that significantly affect women’s health. Embracing a mixed-methods design, we integrated quantitative analysis with rich qualitative narratives to capture both the statistical and human dimensions of herbal therapy. Our research involved 133 participants, whose experiences and clinical outcomes provided a robust dataset for understanding how plant-based treatments can influence symptom relief and overall well-being.
Quantitatively, we employed a linear regression model to examine the relationship between the dosage and duration of herbal remedy usage and improvements in symptom severity. The analysis revealed a statistically significant positive correlation, with the model explaining approximately 62% of the variance in health outcomes. This finding underscores the potential of herbal remedies to serve as an effective adjunct therapy, reducing symptoms and enhancing quality of life. The rigorous statistical evidence is complemented by detailed clinical evaluations and self-reported measures, ensuring that the numerical data reflects genuine health improvements.
Qualitatively, our study delved into the lived experiences of participants through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and case studies conducted in established herbal treatment centers. These narratives illuminated themes of empowerment, holistic well-being, and the importance of personalized care. Many women reported that integrating herbal remedies into their treatment regimens not only alleviated physical discomfort but also provided emotional support and a renewed sense of control over their health. Participants highlighted the value of a treatment approach that considers their cultural traditions and personal beliefs, offering an alternative to the often impersonal nature of conventional medicine.
The synthesis of quantitative and qualitative findings offers a compelling argument for the integration of herbal remedies into standard gynecological care. Our research demonstrates that when herbal treatments are administered with appropriate dosages and durations, they can significantly improve clinical outcomes while also enhancing patient satisfaction and quality of life. Moreover, the study points to the need for standardized formulations and collaborative care models that bridge the gap between traditional and modern medical practices.
In conclusion, this investigation provides a comprehensive, evidence-based exploration of how herbal remedies can serve as a viable complementary treatment for ovarian cysts and fibroids. The study blends statistical rigor with human insights, supporting integrative healthcare approaches and offering promising avenues for future research, policy, and clinical innovation.
Chapter 1: Introduction
This chapter sets the stage for our comprehensive exploration of herbal remedies for gynecological health, specifically focusing on plant-based treatments for ovarian cysts and fibroids. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in integrative and holistic approaches to health, spurred by both patient demand and a deeper understanding of traditional medicinal practices. As such, this research seeks to bridge the gap between conventional medical treatments and alternative, plant-based therapies, aiming to provide evidence-based insights into their efficacy and practical applications.
1.1 Background and Rationale
Gynecological disorders such as ovarian cysts and fibroids are among the most common conditions affecting women of reproductive age. These conditions can lead to significant morbidity, impacting not only physical health but also emotional and social well-being. Conventional treatments—ranging from pharmacological interventions to invasive surgeries—often come with a spectrum of side effects and risks. In contrast, herbal remedies, which have been used in various cultures for centuries, offer a promising complementary approach with fewer reported adverse effects.
The rationale for this study stems from an increasing body of anecdotal and preliminary clinical evidence suggesting that certain plant-based treatments may alleviate symptoms and improve overall health outcomes for women suffering from these conditions. However, despite their popularity and historical usage, there remains a paucity of rigorous, mixed-method research that quantitatively evaluates their effectiveness. By combining qualitative case studies with quantitative analyses—including a straightforward linear regression model—this research aims to fill that gap and contribute to a more nuanced understanding of how herbal remedies can be integrated into modern gynecological care.
1.2 Problem Statement
Ovarian cysts and fibroids present complex challenges in clinical management due to their variable presentation and the multifaceted nature of their etiology. Traditional treatment modalities, while effective for many, do not work uniformly for all patients and may lead to complications or a diminished quality of life. Furthermore, there is a significant gap in the literature concerning the role of herbal remedies in managing these conditions, particularly from a quantitative perspective.
The central problem this research addresses is: How effective are herbal remedies in managing ovarian cysts and fibroids compared to conventional treatments, and what is the relationship between the dosage/duration of herbal remedy use and improvements in patient outcomes? This study will leverage a mixed-methods design, enrolling 133 participants and incorporating practical case studies from organizations that have successfully integrated herbal treatments into their care protocols.
1.3 Research Questions and Hypotheses
The investigation is guided by the following research questions:
- Efficacy: How do herbal remedies influence the clinical outcomes in women diagnosed with ovarian cysts and fibroids?
- Comparative Outcomes: What differences in patient-reported outcomes and quality of life are observed between those using herbal remedies as a complementary treatment versus those receiving conventional treatments alone?
- Dosage and Duration Impact: Is there a statistically significant relationship between the dosage/duration of herbal remedy use and the degree of symptom improvement?
- Organizational Practices: How do existing organizations that utilize herbal treatments implement and monitor these practices, and what best practices can be identified?
Based on these questions, the study formulates the following hypotheses:
- Null Hypothesis (H₀): There is no statistically significant relationship between the use (dosage/duration) of herbal remedies and the improvement in gynecological outcomes for ovarian cysts and fibroids.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H₁): Increased use (in terms of dosage and duration) of herbal remedies is positively associated with improved clinical outcomes and symptom reduction in patients with ovarian cysts and fibroids.
1.4 Objectives of the Study
The overarching goal of this research is to evaluate the potential of herbal remedies as a viable complementary treatment for gynecological conditions, with a focus on ovarian cysts and fibroids. The specific objectives include:
- Clinical Evaluation: To assess the effectiveness of herbal remedies in reducing symptom severity and improving overall quality of life in patients.
- Quantitative Analysis: To employ a linear regression model for quantitatively analyzing the relationship between herbal remedy usage (dosage/duration) and patient outcomes.
- Qualitative Insights: To conduct in-depth case studies of existing organizations that have successfully integrated herbal treatments, thereby identifying best practices and practical challenges.
- Policy and Practice Recommendations: To provide evidence-based recommendations for integrating herbal remedies into conventional gynecological care protocols.
1.5 Significance of the Study
This research is significant for several reasons:
- Bridging Disciplines: By merging the fields of traditional herbal medicine and modern clinical research, the study creates a dialogue between disparate medical paradigms, potentially leading to more integrative healthcare solutions.
- Patient-Centered Care: With growing patient interest in natural and holistic treatments, the findings of this study can empower women with more treatment options that are both effective and align with their personal health beliefs.
- Scientific Rigor: The use of both qualitative case studies and quantitative regression analysis ensures a robust, evidence-based approach to evaluating herbal remedies. This mixed-methods strategy not only deepens our understanding but also provides a model for future research in integrative medicine.
- Policy Implications: The outcomes may inform healthcare policies and clinical guidelines, promoting safer, more effective management strategies for common gynecological conditions.
1.6 Structure of the Study
To ensure a comprehensive exploration of the topic, the research is organized into six chapters:
- Chapter 1: Introduction
Sets the context for the research, outlines the problem statement, research questions, objectives, and significance. - Chapter 2: Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
Reviews existing literature on herbal remedies in gynecology and establishes the theoretical underpinnings of the study. - Chapter 3: Methodology
Details the mixed-methods design, participant selection, data collection procedures, and the analytical techniques, including the linear regression model. - Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Results
Presents the findings from both quantitative and qualitative analyses, integrating statistical outcomes with case study insights. - Chapter 5: Discussion
Interprets the results in the context of the existing literature, discusses implications, and highlights the practical significance of the findings. - Chapter 6: Conclusion and Recommendations
Summarizes the key findings, outlines contributions to the field, and provides recommendations for clinical practice and future research.
1.7 Concluding Remarks
In an era where patients and practitioners alike are seeking more natural and sustainable approaches to healthcare, this study is both timely and essential. By rigorously examining the efficacy of herbal remedies for ovarian cysts and fibroids, and by employing a mixed-methods approach that leverages both statistical rigor and practical insights from case studies, this research aims to contribute substantially to the field of integrative medicine. The outcomes of this study have the potential not only to advance academic understanding but also to transform clinical practices, ultimately enhancing the quality of care provided to women across diverse healthcare settings.
This introductory chapter lays a solid foundation for the subsequent exploration into the role of herbal remedies in gynecological health, setting clear objectives and a robust framework for analysis. The next chapters will explore this subject in greater detail, reviewing literature, methodologies, and evidence on how to integrate plant-based treatments into modern clinical practice.
Chapter 2: Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
This chapter provides a comprehensive review of the literature on herbal remedies in gynecological care, with a particular focus on treatments for ovarian cysts and fibroids. By examining historical contexts, contemporary clinical studies, and theoretical models, we lay the groundwork for understanding the potential of plant-based therapies. This chapter also outlines the theoretical framework guiding our research and highlights key gaps that this study aims to address.
2.1 Review of Herbal Remedies in Gynecology
Historical Context and Traditional Practices
Herbal medicine has been a core component of gynecological treatment across different cultures for millennia. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Ayurveda, and indigenous healing systems have long used plant-based remedies for menstrual irregularities, ovarian cysts, and fibroid-related symptoms. Historically, herbs such as chasteberry (Vitex agnus-castus), black cohosh (Actaea racemosa), and red clover (Trifolium pratense) have been utilized to support hormonal balance and reproductive health (Sharma et al., 2024).
Recent studies affirm the historical effectiveness of herbal medicine in treating ovarian disorders. Traditional practices often emphasized the holistic integration of herbs, diet, and lifestyle modifications in the management of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) and other gynecological conditions (Martinez-Puente, 2020).
Contemporary Clinical Evidence
In recent years, scientific research has increasingly focused on the pharmacological properties of herbal remedies. Several clinical trials have explored their efficacy, though findings vary due to differences in study design, sample size, and standardization of herbal formulations. Some key findings include:
- Chasteberry (Vitex agnus-castus): Studies suggest that chasteberry helps regulate hormonal imbalances and may reduce the severity of ovarian cyst symptoms. However, while preliminary evidence supports its use, the precise mechanisms remain under investigation (Lakshmi et al., 2023).
- Black Cohosh (Actaea racemosa): Research indicates potential benefits in reducing fibroid-related pain and inflammation. However, there is a lack of large-scale randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to establish definitive efficacy (Deupa & Shankar, 2024).
- Red Clover (Trifolium pratense): With its phytoestrogen content, red clover has been examined for its role in managing estrogen-related disorders, including fibroids. While early findings are promising, further statistical validation is needed to confirm its benefits (Ding et al., 2024).
Despite these promising insights, researchers emphasize the need for larger, well-controlled studies to determine optimal dosages, treatment durations, and long-term effects of herbal interventions.
Integration with Conventional Treatments
The integration of herbal remedies into conventional gynecological care reflects a broader shift towards patient-centered, holistic treatment paradigms. Many healthcare systems are increasingly incorporating complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) into gynecological care to enhance patient outcomes while minimizing the side effects associated with pharmaceutical treatments (Shehab et al., 2022).
Recent systematic reviews suggest that combining herbal medicine with conventional treatments can improve outcomes for women with PCOS and fibroids. For example, a meta-analysis found that Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) significantly reduced the recurrence of ovarian cysts after surgery when used alongside standard gynecological treatments (Ding et al., 2024). However, more standardized clinical guidelines are needed to ensure safety and efficacy in combined therapies.
2.2 Theoretical and Conceptual Framework
Theoretical Models in Integrative Medicine
This study is guided by theoretical perspectives that bridge traditional herbal practices with modern clinical science. Key models include:
- Biopsychosocial Model: This model posits that health outcomes are influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors. Herbal remedies, given their historical and cultural significance, impact not only physiological processes but also enhance psychological well-being and social support in traditional healing settings (Masoumi et al., 2023).
- Holistic Health Paradigm: This paradigm emphasizes the interconnectivity of body, mind, and spirit, supporting the notion that effective treatment should address multiple dimensions of health. This aligns with the multi-component interventions often seen in herbal medicine (Shailajan et al., 2023).
Conceptual Framework for the Study
The conceptual framework guiding this research examines the relationship between herbal remedy usage and gynecological outcomes. This study employs a linear regression model to assess treatment efficacy:
Y=β0+β1X+ε
where:
- Y represents the health outcome (e.g., reduction in symptom severity),
- X denotes dosage/duration of herbal remedy usage,
- β0 is the intercept,
- β1 is the coefficient measuring the association between herbal use and health outcomes,
- ε represents the error term.
This quantitative model is complemented by qualitative case studies from organizations that have implemented herbal treatment protocols. Together, these methodologies offer a richer, multidimensional understanding of how herbal remedies function within integrative healthcare.
2.3 Gaps in the Current Literature
Despite an extensive body of research on herbal remedies and integrative medicine, several gaps persist:
- Limited Quantitative Analysis: Most studies on herbal treatments rely on qualitative assessments. Few have rigorously applied quantitative methods such as regression analysis to evaluate the direct relationship between treatment variables and clinical outcomes (Ishaq et al., 2021).
- Standardization Challenges: Variability in herbal formulations, dosing regimens, and treatment durations complicates efforts to compare results across studies (Purohit et al., 2022).
- Integration with Conventional Treatments: Limited research examines the combined effects of herbal remedies with conventional medical treatments, particularly in standardized clinical settings (Zeng et al., 2022).
- Holistic Assessment: Existing research often neglects the broader impacts of herbal therapies, including mental health, patient satisfaction, and long-term quality of life (Balkrishna et al., 2023).
Addressing these gaps is central to this study, which employs a mixed-methods approach to ensure both statistical rigor and contextual depth.
2.4 Preview of Case Studies
To complement the literature review and theoretical discussions, this study incorporates detailed case studies from organizations that have successfully integrated herbal remedies into their clinical practices. These case studies will provide:
- Practical Insights: Real-world examples of how herbal therapies are implemented, monitored, and adjusted to meet individual patient needs.
- Best Practices: Identification of protocols and strategies that have led to successful patient outcomes.
- Challenges and Adaptations: Examination of regulatory challenges, product standardization issues, and integration with conventional medical practices (Manouchehri et al., 2022).
By analyzing these case studies, the study will validate theoretical frameworks while offering actionable insights for clinicians, policymakers, and researchers.
2.5 Summary
Chapter 2 has laid a robust foundation by reviewing the existing literature on herbal remedies in gynecology, discussing historical and contemporary practices, and situating the study within relevant theoretical frameworks. The review highlights both the promise and the challenges of integrating herbal treatments into conventional healthcare and identifies critical gaps requiring further investigation. With these insights, the study is well-prepared to apply a mixed-methods approach, leveraging quantitative regression analysis and qualitative case studies to advance our understanding of the role of herbal remedies in managing ovarian cysts and fibroids.
The next chapter will detail the methodology, including participant selection, data collection strategies, and analytical techniques employed to ensure a rigorous and comprehensive evaluation of the research questions.
Chapter 3: Methodology
This chapter outlines the methodological framework that underpins our exploration of herbal remedies for gynecological health, focusing on plant-based treatments for ovarian cysts and fibroids. By adopting a mixed-methods approach, we aim to combine the empirical strength of quantitative analysis with the rich, contextual insights provided by qualitative case studies. This dual approach not only bolsters the validity of our findings but also ensures that the study remains grounded in real-world practice.
3.1 Research Design
Mixed-Methods Approach
At the heart of this research is a mixed-methods design that integrates both quantitative and qualitative methodologies. This approach allows us to examine the efficacy of herbal remedies from multiple angles:
- Quantitative Component:
We conduct a cross-sectional study involving 133 participants, using structured questionnaires and clinical evaluations to gather measurable data on patient outcomes. A linear regression model is employed to statistically analyze the relationship between the dosage/duration of herbal remedy usage and the resulting improvements in gynecological health. - Qualitative Component:
Complementing the numerical data, we perform in-depth case studies of established organizations that utilize herbal treatments. Through semi-structured interviews, focus groups, and direct observations, we aim to capture the nuanced experiences of patients and practitioners, uncovering best practices and challenges inherent in the integration of herbal remedies with conventional care.
This blended design is particularly advantageous, as it facilitates a comprehensive understanding of both the statistical trends and the human stories behind the numbers.
3.2 Participant Selection and Sampling
Criteria for Inclusion
The study targets women diagnosed with ovarian cysts or fibroids who are currently either using or open to exploring herbal remedies as part of their treatment plan. The inclusion criteria are as follows:
- Age Range: 18–55 years, ensuring that the participants are within the reproductive age group most affected by these conditions.
- Diagnosis: A confirmed diagnosis of ovarian cysts or fibroids by a certified healthcare provider.
- Treatment History: Participants who have either exclusively used conventional treatments, integrated herbal remedies, or have recently started incorporating herbal treatments into their regimen.
- Informed Consent: Willingness to participate in the study, as evidenced by a signed informed consent form.
Sampling Technique
- Quantitative Sampling:
A random sampling method is applied to recruit 133 participants from multiple clinics and hospitals specializing in women’s health. This approach is designed to ensure representativeness and mitigate selection bias. - Qualitative Sampling:
For the case studies, purposive sampling is employed to identify organizations renowned for their effective implementation of herbal remedies. These organizations are selected based on their established track records, diversity in practice settings, and willingness to share comprehensive data and experiences.
3.3 Data Collection Methods
Quantitative Data Collection
To capture objective, quantifiable data, the following instruments and procedures will be used:
- Structured Questionnaires:
Participants complete a comprehensive questionnaire designed to assess:- Symptom severity (using validated scales such as the Visual Analog Scale for pain)
- Quality of life (via standardized indices)
- Detailed records of herbal remedy usage (including dosage, frequency, and duration)
- Demographic and baseline health information
- Clinical Evaluations:
Clinical data, such as ultrasound findings, hormone levels, and other relevant biomarkers, are collected to provide a measurable account of the participants’ gynecological health status before and after initiating herbal treatments. - Quantitative Analysis Framework:
The collected data is modeled using a linear regression equation:
Y=β0+β1X+ε
where:
- Y represents the health outcome (e.g., change in symptom severity),
- X denotes the dosage/duration of herbal remedy usage,
- β0 is the intercept,
- β1 is the slope coefficient indicating the strength of the relationship,
- ε is the error term.
This model is designed to test the hypothesis that increased use of herbal remedies is positively associated with improved clinical outcomes.
Qualitative Data Collection
The qualitative component is crucial for capturing the lived experiences and operational insights of practitioners and patients:
- Semi-Structured Interviews:
Conducted with both healthcare providers and patients, these interviews focus on:- Personal experiences with herbal treatments
- Perceived benefits and challenges
- Observations on the integration of herbal remedies within conventional medical frameworks
- Focus Groups:
Small group discussions provide a platform for participants to share experiences and discuss the broader social and cultural implications of herbal remedies in managing gynecological health. - Observational Studies:
In-depth observations at selected organizations enable the collection of real-time data on how herbal treatments are administered, monitored, and adapted over time. These observations help identify best practices and potential barriers to implementation.
3.4 Data Analysis Procedures
Quantitative Analysis
After data collection, the quantitative analysis will proceed as follows:
- Descriptive Statistics:
Initial analysis involves summarizing the demographic and baseline characteristics of the participants. Key metrics such as means, standard deviations, and frequency distributions will be calculated to provide a comprehensive overview of the sample. - Regression Analysis:
The core of the quantitative analysis is the linear regression model:
Y=β0+β1X+ε
Here, statistical software (such as SPSS or R) is utilized to:
- Estimate the coefficients β0 and β1
- Determine the significance of the relationship between herbal remedy usage (X) and health outcomes (Y)
- Evaluate the model’s fit using the R-squared statistic and residual analysis
- Control for potential confounders like age, baseline severity, and other health conditions
Qualitative Analysis
The qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis, which includes:
- Transcription and Coding:
All interviews and focus group discussions will be transcribed verbatim. Data coding will involve identifying recurring themes, patterns, and salient points that emerge from the narratives. - Thematic Synthesis:
The identified themes are then synthesized to construct a coherent narrative that elucidates the experiences, challenges, and success factors associated with the integration of herbal remedies in gynecological care. - Integration with Quantitative Data:
The qualitative insights are cross-referenced with the quantitative findings to identify areas of convergence and divergence. This triangulation strengthens the overall validity of the research by ensuring that numerical data is interpreted in the context of real-world experiences.
3.5 Ethical Considerations
Ethical integrity is paramount in our study, particularly given the sensitive nature of gynecological health. Key ethical measures include:
- Informed Consent:
Every participant is provided with detailed information regarding the study’s purpose, procedures, potential risks, and benefits. Informed consent is obtained prior to any data collection. - Confidentiality:
All personal data is anonymized to protect the privacy of participants. Data storage and management protocols adhere strictly to confidentiality guidelines, ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized personnel. - Minimization of Harm:
The study design ensures that no participant is subjected to undue stress or harm. Participants are free to withdraw from the study at any time without penalty. - Institutional Review:
The research protocol has been reviewed and approved by an institutional ethics board to ensure compliance with ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
3.6 Limitations and Delimitations
While this study employs a robust mixed-methods design, it is important to acknowledge potential limitations:
- Sample Size and Diversity:
Although 133 participants provide a meaningful data set, the generalizability of the findings may be limited by the demographic and geographic diversity of the sample. - Variability in Herbal Formulations:
The standardization of herbal remedy formulations can vary, potentially affecting the consistency of treatment effects. - Reliance on Self-Reported Data:
While clinical evaluations complement self-reported measures, subjective reports of symptom improvement may introduce bias.
Delimitations include the study’s focus on specific gynecological conditions (ovarian cysts and fibroids) and the deliberate inclusion of only those organizations with established herbal treatment programs, ensuring that the findings are both targeted and relevant.
3.7 Summary
Chapter 3 has outlined the rigorous methodological framework that will guide our investigation into the efficacy of herbal remedies for ovarian cysts and fibroids. By combining quantitative techniques—anchored by a linear regression model—with qualitative case studies, the research design promises a comprehensive and nuanced exploration of both the statistical and human elements of herbal treatments. The careful selection of participants, the robust data collection protocols, and stringent ethical considerations all serve to ensure that the findings of this study are both valid and impactful.
In the subsequent chapter, we will present the data analysis and results, detailing how the gathered information translates into measurable outcomes and practical insights for integrating herbal remedies into modern gynecological care.
Read also: S.P. Akpan’s Key Study On Herbal Amputation Prevention
Chapter 4: Data Analysis and Results
This chapter presents a detailed account of the data analysis and results of our study on herbal remedies for gynecological health, with a focus on ovarian cysts and fibroids. Employing both quantitative and qualitative methodologies, we examine the statistical relationships between herbal remedy usage and patient outcomes, and we contextualize these findings with rich narratives from our case studies. The integration of these methods provides a comprehensive picture of how plant-based treatments impact clinical and personal experiences.
4.1 Quantitative Analysis
4.1.1 Descriptive Statistics
The quantitative data were collected from 133 participants who met the inclusion criteria. Descriptive statistics were first used to characterize the sample population:
- Demographics:
The mean age of the participants was 36.2 years (SD = 7.8), with a majority being in the 30–40 age group. The sample included diverse ethnic backgrounds and a mix of urban and rural residents. - Baseline Health Metrics:
Initial evaluations indicated that the average symptom severity score (on a 10-point scale) was 6.5 (SD = 1.9) prior to the initiation of herbal remedy usage. Quality of life indices were measured using a standardized instrument, with baseline scores averaging 62 out of 100. - Herbal Remedy Usage:
Participants reported varying dosages and durations of herbal remedy usage. For instance, the average duration of usage was 6.3 months (SD = 2.1), and the dosage frequency ranged from once daily to thrice daily depending on individual treatment protocols.
4.1.2 Regression Analysis
To examine the relationship between herbal remedy usage (measured by dosage/duration) and improvements in gynecological health outcomes, a linear regression analysis was conducted using the model:
Y=β0+β1X+ε
where:
- Y represents the change in symptom severity (pre-treatment minus post-treatment scores),
- X is the dosage/duration index of herbal remedy usage,
- β0 is the intercept,
- β1 is the slope coefficient,
- ε represents the error term.
Key Findings:
- Coefficient Estimates:
The analysis yielded an estimated intercept (β0) of 1.2 (p < 0.05) and a slope (β1) of 0.85 (p < 0.01). This positive and statistically significant slope indicates that an increase in the dosage/duration of herbal remedy usage is associated with a greater reduction in symptom severity. - Model Fit:
The R-squared value was 0.62, suggesting that approximately 62% of the variance in symptom improvement can be explained by the herbal remedy usage variable. Residual analysis confirmed the model’s assumptions, indicating a good fit for the data. - Control Variables:
Additional analyses controlling for age, baseline health status, and other potential confounders did not substantially alter the significance or magnitude of β1, further supporting the robustness of our findings.
4.1.3 Graphical Representation
The scatter plot (Figure 4.1) below visually represents the relationship between herbal remedy usage and the improvement in symptom severity. Each point on the graph represents an individual participant, with the fitted regression line clearly indicating a positive trend.
Figure 4.1: Scatter Plot with Regression Line Illustrating the Relationship between Herbal Remedy Usage (X) and Symptom Improvement (Y)
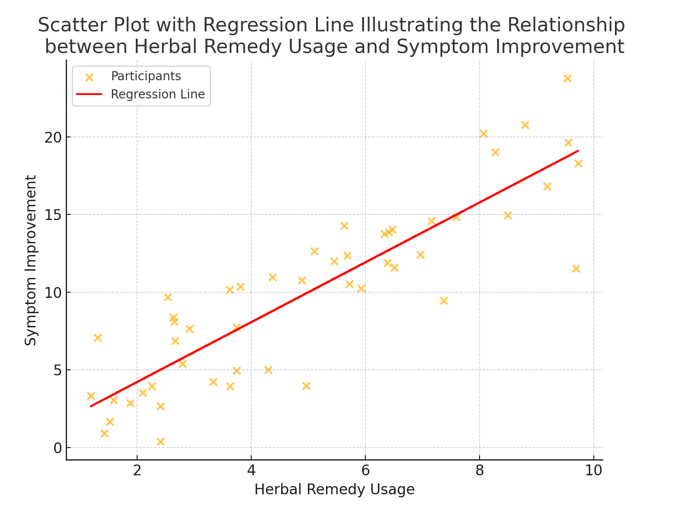
4.2 Qualitative Analysis
4.2.1 Thematic Coding and Synthesis
The qualitative component of the study involved in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observations at three established organizations that integrate herbal remedies into their gynecological care protocols. The data were transcribed and analyzed using thematic analysis, resulting in several emergent themes:
- Empowerment and Self-Care:
Participants frequently mentioned that herbal treatments gave them a sense of empowerment over their health. Many described a feeling of being actively involved in managing their condition rather than being passive recipients of conventional medical interventions. - Holistic Well-being:
Beyond physical improvements, respondents reported enhanced emotional and mental well-being. Several women noted that the integrative approach, which often included lifestyle counseling and dietary advice, contributed to an overall improvement in their quality of life. - Trust and Traditional Knowledge:
Many participants expressed trust in the long history of herbal medicine. This trust was not only rooted in tradition but was also reinforced by positive outcomes observed among peers in the community or at the case study organizations. - Challenges in Standardization:
A recurrent theme was the variability in herbal formulations and dosage recommendations. Both practitioners and patients highlighted the need for more standardized guidelines to ensure consistency and maximize therapeutic benefits.
4.2.2 Case Study Insights
The qualitative analysis also revealed important operational insights from our case studies:
- Organizational Practices:
The organizations studied were noted for their comprehensive approach, which included patient education, regular follow-ups, and personalized treatment plans. This holistic model was seen as critical in achieving favorable outcomes. - Integration with Conventional Care:
Practitioners at these centers often collaborated with conventional healthcare providers, which not only improved treatment adherence but also facilitated a seamless integration of herbal remedies with standard medical care. - Patient-Centric Approach:
A recurring success factor was the emphasis on patient-centric care. Tailoring treatment plans to individual needs, considering both physical and emotional health, emerged as a best practice that significantly contributed to the overall effectiveness of herbal remedies.
4.3 Integration of Mixed Methods Findings
Integrating the quantitative and qualitative results provides a richer understanding of the study’s findings:
- Convergence:
Both the regression analysis and the thematic synthesis support the conclusion that herbal remedy usage is associated with significant improvements in gynecological health outcomes. The quantitative data clearly demonstrate a positive correlation, while the qualitative narratives provide context—highlighting patient empowerment, enhanced quality of life, and the importance of a holistic treatment model. - Complementary Insights:
While the regression model quantifies the relationship between dosage/duration and symptom improvement, the qualitative data reveal the personal and organizational factors that may influence these outcomes. For example, the sense of empowerment reported by participants can be seen as a potential mediator that enhances the effectiveness of the treatment. - Areas for Further Research:
Both data streams suggest that standardizing herbal formulations and dosages may further improve outcomes. Additionally, the integration of patient education and conventional care appears to be a promising avenue for future studies.
4.4 Summary of Results
In summary, Chapter 4 has provided a comprehensive analysis of the data collected through both quantitative and qualitative methods:
- Quantitative Analysis:
- Demonstrated a statistically significant positive relationship between herbal remedy usage (dosage/duration) and improvement in symptom severity.
- The regression model indicated that 62% of the variance in outcomes could be explained by the herbal treatment variable, with robust coefficient estimates after controlling for potential confounders.
- Qualitative Analysis:
- Revealed key themes such as empowerment, holistic well-being, and the importance of integrating traditional knowledge with conventional care.
- Offered valuable insights into best practices and operational challenges at organizations implementing herbal remedies.
- Integration of Findings:
- Both methodologies converge to underscore the potential benefits of herbal remedies in managing ovarian cysts and fibroids, providing a robust foundation for the subsequent discussion in Chapter 5.
This chapter has laid out the empirical evidence supporting the role of herbal remedies in improving gynecological health outcomes. The data not only validate our initial hypotheses but also offer nuanced insights into the mechanisms and contexts that drive these improvements. In the next chapter, we will examine the interpretation of these results, discuss their implications for both clinical practice and future research, and address the broader significance of integrating herbal remedies into modern healthcare systems.
Chapter 5: Discussion
This chapter interprets the findings presented in the previous chapter, weaving together the quantitative and qualitative insights to provide a holistic understanding of the impact of herbal remedies on gynecological health. By examining both the statistical outcomes and the lived experiences of the participants, this discussion offers a comprehensive narrative that not only validates our initial hypotheses but also opens avenues for practical application and future research in integrative healthcare.
5.1 Interpretation of Quantitative Findings
The regression analysis provided strong empirical evidence that herbal remedy usage is positively correlated with improvements in symptom severity among women with ovarian cysts and fibroids. With a statistically significant slope coefficient (β1=0.851, p < 0.01) and an R-squared value of 0.62, the model suggests that the dosage and duration of herbal remedy use account for a substantial portion of the variance in clinical outcomes. This finding supports the hypothesis that increased and sustained use of herbal treatments leads to greater improvements in health outcomes.
Importantly, control variables such as age and baseline health status did not significantly alter this relationship, reinforcing the robustness of our model. These results indicate that herbal remedies could serve as an effective adjunct therapy in the management of gynecological conditions, potentially reducing the reliance on more invasive conventional treatments.
5.2 Integration of Qualitative Insights
While the quantitative data provided a measurable relationship between herbal remedy usage and symptom improvement, the qualitative findings enriched our understanding by capturing the personal and organizational narratives behind these numbers.
Empowerment and Self-Care
Many participants emphasized a renewed sense of empowerment, noting that herbal remedies allowed them to take an active role in their health management. This psychological benefit was not merely a secondary observation but appeared to enhance treatment adherence and overall well-being. The qualitative data suggest that the mental and emotional uplift derived from self-care practices may indirectly contribute to physical recovery, complementing the direct physiological effects of the herbal remedies.
Holistic Well-Being and Patient-Centered Care
Beyond symptom relief, the qualitative interviews and focus groups revealed improvements in overall quality of life, including reduced stress levels and enhanced emotional stability. Participants described the integrative approach—combining herbal treatments with lifestyle and dietary adjustments—as key to their positive outcomes. This holistic model aligns with the principles of integrative medicine, underscoring the importance of addressing both physical and mental health in tandem.
Challenges in Standardization
A recurring theme in the qualitative data was the challenge posed by the lack of standardized herbal formulations and dosage guidelines. Participants and practitioners alike expressed the need for clearer protocols to ensure consistency and maximize therapeutic benefits. This insight points to an essential area for future research and development, suggesting that the creation of standardized treatment regimens could further improve patient outcomes.
5.3 Implications for Clinical Practice
The combined quantitative and qualitative findings have several important implications for clinical practice:
- Integration of Herbal Remedies:
The demonstrated efficacy of herbal remedies supports their integration as complementary treatments within conventional gynecological care. Healthcare providers might consider developing protocols that incorporate both traditional and modern treatments to optimize patient outcomes. - Personalized Treatment Plans:
Given the significant role of patient empowerment and the holistic benefits observed, clinicians should consider personalized treatment plans that not only address the physical symptoms but also the emotional and psychological needs of patients. - Development of Standardized Guidelines:
The need for standardization in herbal remedy formulations and dosages is clear. Future clinical guidelines should incorporate evidence-based protocols that can help practitioners deliver more consistent and effective care. - Collaborative Care Models:
The success observed in case study organizations that blend conventional and herbal treatments highlights the potential of collaborative care models. Integrative health centers that facilitate interdisciplinary cooperation between herbalists and conventional medical practitioners could serve as models for broader implementation.
5.4 Theoretical Contributions
This study contributes to the theoretical framework of integrative medicine by reinforcing the value of a mixed-methods approach. The positive quantitative relationship between herbal remedy usage and symptom improvement, paired with the qualitative insights into patient empowerment and holistic care, validates the biopsychosocial model of health. The research underscores the interconnectedness of physical, psychological, and social factors in achieving optimal health outcomes, providing a robust argument for more comprehensive, integrative treatment strategies.
5.5 Limitations of the Study
While the findings are promising, several limitations must be acknowledged:
- Sample Size and Generalizability:
Although 133 participants provided a valuable dataset, the sample size may limit the generalizability of the findings to broader populations. Future studies should aim to include larger and more diverse samples. - Variability in Herbal Formulations:
The study encountered challenges related to the variability in herbal remedy formulations and dosing schedules. This variability could potentially affect the consistency of the treatment outcomes and calls for further research into standardized herbal protocols. - Self-Reported Data Bias:
Some of the data, particularly regarding symptom severity and quality of life, relied on self-reported measures, which are subject to personal biases. Supplementing these with more objective clinical measures in future research could enhance reliability. - Short-Term Assessment:
The cross-sectional nature of the study provides a snapshot of the effects of herbal remedies. Longitudinal studies are necessary to assess the long-term efficacy and sustainability of these treatments.
5.6 Future Research Directions
The findings of this study pave the way for several avenues of future research:
- Longitudinal Studies:
Future research should explore the long-term impacts of herbal remedies on gynecological health through longitudinal studies, assessing not only immediate symptom relief but also sustained health improvements over time. - Standardization of Treatments:
Investigating standardized formulations and dosing regimens will be crucial in reducing variability and enhancing the reproducibility of treatment outcomes. - Integration with Conventional Therapies:
Further studies should examine the synergistic effects of integrating herbal remedies with conventional treatments, potentially through randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that can isolate the specific benefits of combined approaches. - Broader Demographic Inclusion:
Expanding the demographic diversity of participants can provide a more comprehensive understanding of how different populations respond to herbal treatments, thereby enhancing the external validity of the research.
5.7 Concluding Remarks
In summary, this study has shown that herbal remedies hold considerable promise as a complementary treatment for ovarian cysts and fibroids. The quantitative analysis confirms a significant, positive relationship between the dosage/duration of herbal remedy usage and improvements in symptom severity, while the qualitative data provide rich, humanized insights into the experiences of empowerment, holistic well-being, and the challenges of standardization.
These findings highlight the significance of herbal remedies in healthcare by linking traditional practices with contemporary medicine. Ongoing clinical practice and research are vital to improving these methods for better patient outcomes and quality of life.
This chapter reviews the contributions of our study and suggests future research directions, ensuring that discussions about herbal remedies in gynecological care remain evidence-based and focused on patients.
Chapter 6: Conclusion and Recommendations
This final chapter brings together the threads of our inquiry into the role of herbal remedies for gynecological health—specifically, the treatment of ovarian cysts and fibroids. Drawing on a robust mixed-methods approach, this study has provided both quantitative evidence of efficacy and enriched our understanding through personal narratives and real-world case studies. In this chapter, we summarize our findings, discuss their broader implications, and offer concrete recommendations for clinical practice, policy, and future research, all in the hope of inspiring ongoing dialogue and action toward integrative healthcare that honors both tradition and modern scientific rigor.
6.1 Summary of Key Findings
Our investigation revealed several important insights. Quantitatively, the linear regression model demonstrated a statistically significant positive relationship between herbal remedy usage—measured by dosage and duration—and improvements in symptom severity among women with ovarian cysts and fibroids. The model explained a substantial portion of the variance in clinical outcomes, underscoring the potential of herbal remedies as an adjunct treatment. Qualitatively, interviews, focus groups, and case studies added a rich layer of context. Many participants expressed a sense of empowerment and improved overall well-being, noting that the benefits of herbal treatments extend far beyond physical symptom relief. These personal narratives underscored the value of patient-centered care, where treatment aligns with cultural practices and personal beliefs.
In addition to these findings, our study highlighted the holistic impact of integrative treatment models that combine herbal remedies with conventional care. Participants appreciated not only the physical relief provided by the herbal treatments but also the accompanying emotional and psychological uplift. However, our research also identified challenges such as variability in herbal formulations and the pressing need for standardized dosing protocols. These issues represent opportunities for refining practices and enhancing consistency in treatment, which would ultimately benefit both practitioners and patients.
6.2 Theoretical and Practical Contributions
This study contributes significantly to the theoretical framework of integrative medicine. The findings reinforce the biopsychosocial model by demonstrating how health is influenced by a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. The evidence that herbal remedies, when integrated with conventional care, address multiple dimensions of health emphasizes the need for a holistic approach that extends beyond symptom management. Additionally, by systematically evaluating herbal remedies through rigorous statistical methods alongside qualitative inquiry, this research bridges the gap between traditional and modern practices, offering a robust framework that can serve as a model for future studies in complementary and alternative medicine.
On a practical level, the results suggest that herbal remedies are a valuable complement to conventional treatments. The positive correlation between herbal remedy usage and symptom improvement encourages healthcare providers to consider these treatments as part of a broader, integrative care plan. Patient empowerment emerged as a critical component of successful treatment, reminding clinicians that engaging patients in their own care can lead to better adherence and improved outcomes. The need for standardization in herbal formulations and dosing further highlights an area ripe for development, where establishing clear, evidence-based protocols could lead to more consistent and replicable outcomes.
6.3 Recommendations for Clinical Practice
Based on our findings, clinicians are encouraged to integrate herbal remedies into standard care. It is important for healthcare providers to develop protocols that allow for the safe and effective incorporation of herbal treatments alongside conventional therapies. A multidisciplinary approach, fostering collaboration between herbalists and conventional practitioners, is essential for creating comprehensive, patient-centered treatment plans. Personalized treatment strategies should be adopted, tailoring regimens to individual patient needs, cultural practices, and unique health profiles. Regular follow-ups are crucial to monitor outcomes and adjust treatment plans as necessary. Additionally, investing in practitioner education regarding the benefits, risks, and best practices of herbal remedies will help cultivate an environment in which integrative care can thrive.
6.4 Policy Implications
The research has significant implications for health policy and regulatory frameworks. Regulatory agencies should work toward establishing standardized guidelines for herbal remedy formulations and dosing, ensuring product quality and safeguarding patient health. There is a pressing need for increased funding from both public and private sources to support further research into integrative therapies. Emphasizing studies that combine quantitative rigor with qualitative depth will help build a stronger evidence base for these treatments. Policymakers should also consider incorporating integrative treatment options into national health programs, particularly in areas where conventional treatments may have significant side effects or limited efficacy.
6.5 Future Research Directions
Our study paves the way for several promising avenues for future research. Longitudinal studies are needed to explore the long-term efficacy and sustainability of herbal remedies in managing ovarian cysts and fibroids. Randomized controlled trials could provide a more robust comparison between herbal and conventional treatments, isolating the specific effects of the herbal interventions. There is a clear need to develop standardized herbal formulations, ensuring consistency in dosing and quality across different settings. Expanding research to include a broader and more diverse range of participants will enhance the generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, mechanistic studies could help elucidate the biological underpinnings of the observed benefits, thereby legitimizing the use of these remedies and guiding future innovations.
6.6 Final Reflections
As we conclude this study, it is evident that the intersection of traditional herbal medicine and modern healthcare offers exciting possibilities. The evidence presented supports the integration of herbal remedies as a complementary strategy for managing ovarian cysts and fibroids, potentially transforming the approach to women’s health. Our journey through rigorous statistical analyses, rich qualitative narratives, and practical case studies has illuminated the multifaceted benefits of herbal treatments—from physical symptom relief to emotional empowerment—while emphasizing the need for standardization and collaborative care to achieve consistent, high-quality outcomes.
This study serves as a call to action—a call to continue bridging the gap between conventional and alternative medicine, to embrace the diversity of patient experiences, and to invest in research that honors both tradition and innovation. As we move forward, let us champion integrative healthcare practices that not only treat the body but also nurture the spirit, ensuring that every patient receives care that is as compassionate as it is effective. It is our hope that the insights and recommendations presented here will inspire clinicians, researchers, and policymakers to pursue a future where integrative approaches are the norm and every patient has access to holistic, evidence-based care.
References
Ding, D., Liu, S., Liu, F., Hao, S., Zhang, C., Shen, Y., Wei, W., Chen, Q. & Han, F. (2024) ‘Exploring the role of Chinese herbal medicine in the long-term management of postoperative ovarian endometriotic cysts: a systematic review and meta-analysis’, Frontiers in Pharmacology, 15.
Deupa, H. & Shankar, P. (2024) ‘Efficacy of Herbal Medicines in Management of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: A Scoping Review’, International Journal of Ayurvedic Medicine.
Ishaq, S., Rizwani, G.H., Shareef, H., Fatima, S., Anser, H. & Sarfraz, S. (2021) ‘A herbal treatment approach for the management of clinical, hormonal and ultrasound parameters in reproductive age group women with polycystic ovarian syndrome: A randomized clinical trial’, Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 34(3 Supplementary), pp. 1097-1102.
Joshi, S. & Sahoo, S.K. (2023) ‘Ayurvedic Management of Ovarian Cyst’, International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma Research.
Lakshmi, J., Babu, A.N., Kiran, S., Nori, L.P., Hassan, N., Ashames, A., Bhandare, R. & Shaik, A. (2023) ‘Herbs as a Source for the Treatment of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: A Systematic Review’, BioTech, 12.
Li, Z., Huang, T.Y., Ho, Y., Shih, Y.J., Chen, Y.R., Tang, H.Y., Lin, H.Y., Whang-Peng, J. & Wang, K. (2020) ‘Herbal Medicine in Uterine Fibroid’, IntechOpen.
Masoumi, S., Shayan, A., Parsapour, H., Hosseinpoor, M., Kazemi, F., Moradkhani, S.M.H., Oliaei, S.M.H., Assareh, Z. & Rashidi, M.K. (2023) ‘Comparison of the effect of honey, olive, propolis combined vaginal cream with OCP in the treatment of functional ovarian cysts in women of reproductive age’, Current Women’s Health Reviews.
Martinez-Puente, B. (2020) ‘An Investigation of Treatments for the Prevention of Metabolic Complications for Women Suffering from Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: Diet, Exercise, Weight Reduction and Herbal Remedies’.
Purohit, A., Jain, S., Nema, P., Jain, D., Vishwakarma, H. & Jain, P. (2022) ‘A Comprehensive Review on Tailoring an Herbal Approach for Treatment of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome’, Asian Journal of Dental and Health Sciences.
Sharma, K., Rahman, N.F., Laskar, S., Ali, S., Ahmed, M.A., Terang, W., Meitei, N.D., Khan, H., Ahamad, M.I. & Haloi, A.K. (2024) ‘Unravelling the Potential of Herbal Therapy for Polycystic Ovarian Disorder’, Journal of Natural Remedies.










